Cancer has arisen as a major public health concern in India, marked by uncontrolled cell development. The World Health Organisation (WHO) estimates that India has approximately 1.4 million new cancer cases and 0.8 million cancer-related deaths each year. This concerning trend emphasises the critical need for innovative and effective therapeutic solutions. Robotic surgery has emerged as a beacon of hope in this scenario, revolutionising cancer therapy in India.
Understanding Robotic Surgery
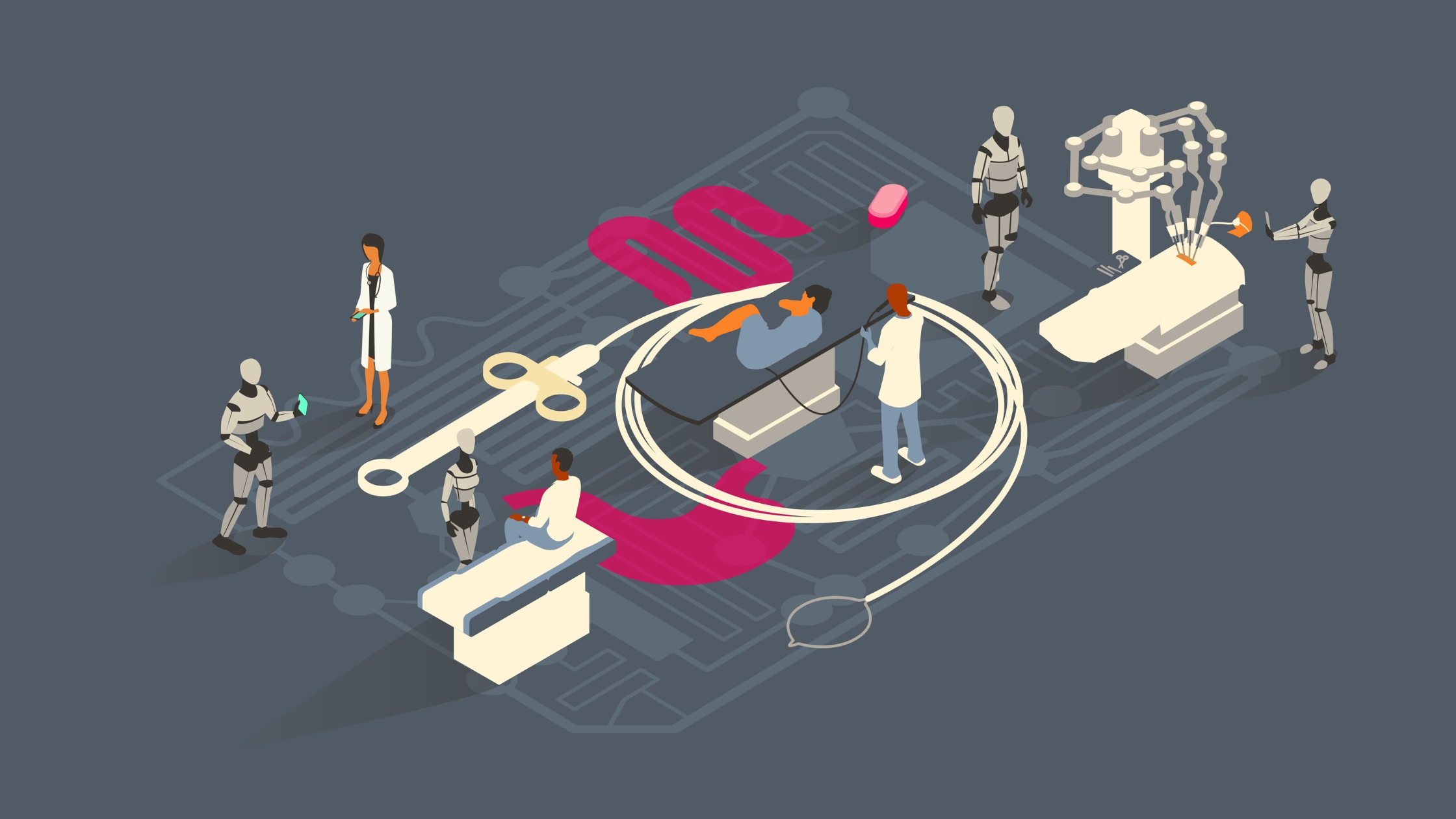
Robotic surgery, also known as robot-assisted surgery, is a minimally invasive surgical method in which computer-controlled robotic systems are used to execute difficult procedures with greater precision and dexterity. In contrast to traditional open procedures, which use huge incisions, robotic surgery uses smaller incisions, resulting in less discomfort, scarring, and hospital stays.
The history of robotic surgery may be traced back to the 1990s, with considerable technological advances over the years. Robotic surgical systems now include high-definition 3D visualisation, motion scaling, and tremor filtering, giving doctors an unprecedented view of the operative field and allowing precise control of surgical tools.
Robotic Surgery's Key Components and Technologies
- Surgical Table: The surgeon sits at the console, observing the operating field in 3D high-definition and precisely controlling the robotic arms.
- Robotic Arms: These arms imitate the surgeon's hand movements, offering significantly greater dexterity and precision than human hands.
- Surgical Instruments: The robotic arms are equipped with a number of specialised surgical equipment that allow for a wide range of treatments.
- Imaging System: A high-definition 3D camera visualises the operation field in real-time.
The Current Landscape of Cancer Treatment in India
Cancer treatment in India confronts a variety of obstacles, including an increase in patient numbers, limited access to specialised care, and a dependence on traditional treatment approaches, which frequently include significant surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. While these therapies are successful, they can have serious side effects and problems. Traditional cancer treatments frequently have various limitations:
- Open surgery: Large incisions can cause substantial pain, scarring, and longer recovery times during open surgery.
- Chemotherapy: Systemic medication therapy can have systemic adverse effects, affecting both healthy and malignant tissues.
- Radiation therapy: While radiation therapy is beneficial in many situations, it can damage healthy tissues surrounding the tumour site, leading to long-term consequences.
The necessity for improved and precise treatment alternatives becomes clear, prompting the incorporation of robotic surgery into the cancer treatment process.
The Role of Robotic Surgery in Cancer Treatment
Robotic surgery has emerged as a game changer in cancer treatment, providing a minimally invasive, precise, and successful method of tumour removal:
- Precision and accuracy: Robotic arms give surgeons greater dexterity and precision, allowing for more accurate tumour removal while minimising injury to healthy tissues in the surrounding area. This precision is especially important in delicate procedures involving vital structures like nerves and blood arteries. For example, with robotic prostate surgery, the physician can more precisely protect nerves crucial for erectile function, lowering the likelihood of post-operative impotence.
- Minimally invasive nature: When compared to traditional open surgery, robotic surgery uses tiny incisions, resulting in less surgical trauma, less blood loss, and faster recovery times.
- Reduced postoperative problems and side effects: Because robotic surgery is less invasive, the risk of postoperative complications such as infections and wound healing disorders is considerably reduced.
Advancements in Robotic Surgery
The field of robotic surgery is constantly expanding, with new systems and technologies being introduced to expand its potential. These improvements improve the precision, efficacy, and usefulness of robotic surgery in cancer treatment:
- Latest robotic surgical systems: The most recent robotic surgical systems provide better dexterity, improved visualisation, and the ability to execute more difficult surgeries.
- Dual-console surgery: This approach allows two surgeons to operate on different robotic consoles at the same time, allowing for more sophisticated and delicate surgeries.
- Fluorescence-guided surgery: This approach highlights tumours and important structures with fluorescent dyes, improving surgical precision.
- Robotic-assisted natural orifice surgery: This minimally invasive technique minimises incisions by using natural orifices, such as the mouth or vagina, as entrance points for surgical tools.
Challenges and Considerations: Addressing Concerns and Ensuring Accessibility
While robotic surgery has great promise for cancer therapy in India, certain obstacles must be overcome. The cost of robotic surgical equipment can be prohibitively expensive, and skilled surgeons are currently few. Furthermore, teaching patients about robotic surgery is critical in empowering them to make informed treatment decisions. Healthcare professionals must give clear and concise information regarding the benefits, dangers, and costs of robotic surgery, as well as address typical patient concerns and misconceptions about cost, safety, and efficacy.
Future Opportunities and Innovations
Ongoing robotic surgery research and development has enormous promise for the future of cancer treatment:
- Robotic surgery powered by AI: Artificial intelligence (AI) is poised to transform robotic surgery by providing real-time image processing, predictive modelling, and robotic arm assistance.
- Nanorobotics: Nanorobotic technology has the potential to provide highly targeted and precise cancer treatment by allowing therapeutic substances to be delivered directly to tumour cells.
- Robotic medication delivery: Robotic systems are being developed to deliver pharmaceuticals and therapeutic agents with pinpoint accuracy, reducing adverse effects and increasing treatment efficacy.